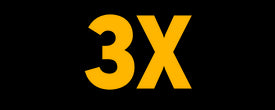AMINO ACIDS
Crickets and grubs have all of the essential amino acids (the building blocks for a complete protein). Exceeding AAFCO canine maintenance requirements!

CHOLINE
The dog’s body uses choline for a variety of functions that benefit not only the brain, but other systems as well.

FATTY ACIDS
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are those fatty acids that a species requires that it can’t make from other sources. Linoleic acid is an example of an EFA for dogs.

MINERALS
Dogs need minerals and insect protein delivers!

B VITAMIN
The vitamin B Complex includes various types of B vitamins.
Vitamin B Complex is very important for the dog’s muscle and nerve functions.

PROTEIN DIGESTIBILITY IN DOGS
Digestibility refers to the percentage of nutrients that a dog absorbs into their body during the process
of digestion. Proteins are large molecules made up of 20 amino acids. While dogs produce about half of these
amino acids themselves, the other half, called essential amino acids, must be provided through the diet.
Digestibility refers to the relative amount of nutrients within the diet that become available to the body
after digestion and absorption. The protein digestibility in dogs for a food product is determined through
feeding trials.
Canine nutritionists accept that the minimum target is 80 percent, with ideal values ranging between 80 and
90 percent. Feeding diets exceptionally high in digestibility isproblematic. A dog’s large intestine is
adapted to expect some undigested foods such as plant fibers and cartilaginous materials. Depriving the
colon of these foods influences colonic health and reduces fecal bulk.